The recency and primacy effect are both parts of the serial position effect, which predicts how items from a list are remembered, based on their position in that list. The first and last items on a list are generally remembered the best.
Serial-position effect is the tendency of a person to recall the first and last items in a series best, and the middle items worst.
This guide will teach you:
1. Recency Effect
One explanation is that these items are still present in working memory. An additional explanation is related to the context: if tested immediately after rehearsal, the current temporal context can serve as a retrieval cue, which would predict more recent items to have a higher likelihood of recall.
The recency effect occurs more commonly when the response options are given orally. This is thought to be because when the respondent is listening to all of the options, the later options disrupt the respondent’s consideration of earlier options.
2. Primacy Effect
A suggested reason is that the initial items presented are most effectively stored in long-term memory because of the greater amount of processing devoted to them. (The first list item can be rehearsed by itself; the second must be rehearsed along with the first, the third along with the first and second, and so on.) This reaction is enhanced when presented slowly. Longer lists have been found to reduce our capability to remember the first words of a list.
This effect is most evident when answers are shown visually. Options that are presented later tend to not be considered in the same way as the earlier options.
3. Minimizing primacy and recency effect in your survey
In order to reduce survey bias arising from these two effects, the easiest thing you can do is to randomize the answer options. The shuffle answers feature changes the order of the answer options for each respondent, so when analyzing all response data, you’ll be able to see the average behavior.
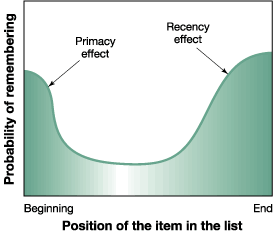
From the graph below you can see where both effects occur. We tend to remember more the last words, especially when the length of the list increases.
4. Example
Use this list of random words to test out your memory. Try reading it out to someone nearby, and see which words they remember the best. When the list is read out, there will be a tendency to recall the later words better, the recency effect.
To test out the primacy effect, show someone the list of words, and then remove the list and ask them to recall the words. Since the list was presented to them in a visual manner, they saw the words rather than hearing them, the primacy effect is likely to be more apparent and the earlier words are likely to be remembered better.
| Blue | Coat | Fortune | Kick | Complex | Finance | Indoor |
| Budget | Cycle | Matrix | Transform | Exceed | Hobby | Slide |
What's next?
- Survey completion rate: When calculating the survey completion rate, the calculation only takes to account those people who had some interaction with the survey, meaning that they actually started it. We don’t count the number of people who were invited and ignored the invitation.
Survey Response Rate: In survey research, response rate, also known as completion rate or return rate, is the number of people who completed the survey divided by the number who received an invitation or were in the sample. It is usually expressed in the form of a percentage.
- Net Promoter Score Question (NPS): is an index ranging from -100 to 100 that measures the customer's willingness to recommend a company's products or services to others. It is used as a proxy for gauging the customer's overall satisfaction with a company's product.
